What is choledocholithiasis?
The ducts mainly involved are the common bile duct, the cystic duct, and the common hepatic duct.
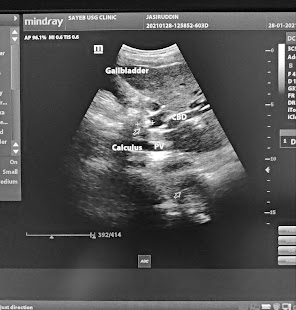
The common bile duct ( CBD ) is mainly involved in Choledocholithiasis.
The common bile duct ( CBD ) is a tube carrying the bile formed in the gall bladder to the third part of the duodenum at the junction of the ampulla of Vater. At this junction, the main pancreatic duct is also open.
What are the types of bile duct stones?
A. Types of bile duct stone on the basis of their site of formation:
Two types of stones are found in the common bile duct -
1. Primary bile duct stones
2. Secondary bile duct stones
B. Types of stones on the basis of their chemical nature:
2. Pigment stones – rare, formed of bile pigment bilirubin as calcium bilirubinate salt. These types of stones are brown in color.
3. Mixed stones – These are a combination of cholesterol, bile pigments calcium, phosphates, protein, and cysteine.
What are the risk factors of choledocholithiasis?
The risk factors are following:
- 4F
Fatty
Forty
Fertile
- Oral contraceptive pills ( OCP )
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Family history
- Rapid weight loss
- Diet -
Refined carbohydrates in the diet.
Low fibers diet.
- Chronic liver disease – cirrhosis
- Infection –Cholangitis, Cholecystitis
- Hemolytic disease – sickle cell disease, hereditary spherocytosis
What is the Pathophysiology of choledocholithiasis?
These are:-
- Metabolic factors –
- Reflux factors -
- Stasis factors -
- Infective factors -
Metabolic factors:-
Reflux factors:-
Stasis factors:-
Infective factors:-
What are the Causes of Choledocholithiasis?
Causes of cholesterol stones:-
When the ratio of bile acid and cholesterol in the bile juice decreases, the precipitation of cholesterol occurs which in turn leads to the formation of cholesterol stones.
The reason being:
Excessive cholesterol.
Excessive bilirubin.
Less bile salts.
Parenteral nutrition.
Prolong fasting
Infections
Causes of pigment stones:-
When excessive bile pigments are excreted in the bile juice the precipitation of bile occurs and pigment stones are formed.
The reason being:
Haemolytic diseases – sickle cell disease, haemolytic anemia, septic haemolysis, malaria.
Cirrhosis
Infections
What are the signs and symptoms of choledocholithiasis?
Pain – Present is predominantly felt in right hypochondrium, and may be present in the epigastric region, and is radiating to the right shoulder and back. Pain is exacerbated after fatty foods.
On examination, tenderness is elicited in right hypochondrium.
Fever with chill -
Jaundice - Icterus ie yellowish discoloration of the sclera is present.
Itching of the body – due to obstructive jaundice.
Loss of appetite -
Dyspepsia -
Nausea and vomiting -
Clay-colored stool -
Dark yellowish colored urine -
Charcot’s triad:
Abdominal pain – in the right hypochondrium.
Fever with chill
Fluctuating Jaundice – due to obstruction of the common bile duct.
What are the Complications of choledocholithiasis?
Hepatitis – inflammation, and impairment of liver function
Pancreatitis – inflammation pancreas
Cholangitis – Inflammation of the biliary tract
Cholecystitis – Inflammation of gall bladder.
Hydro-hepatosis – gross dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary canaliculi is also seen. Although this is a rare condition.
Peritonitis – when stone ulcerate to peritoneal cavity and infection of the perineum is leading to peritonitis.
What is the Diagnosis of choledocholithiasis?
Haematology -
Haemoglobin
Total leukocyte count
Differential leukocyte count
Urine examination –
Bile pigment may be seen.
Biochemistry –
Liver function test ( LFT ) -
Kidney function test ( KFT ) -
Imaging/Radiology:
Transabdominal ultrasound
Abdominal CT scan
Endoscopic ultrasound
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography ( ERCP )
Magnetic resonance cholangiography ( MRCP )
Magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI )
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram ( PTCA)
Hydroxyl iminodiacetic acid scan ( HIDA SCAN )
What is the management/treatment of choledocholithiasis?
Conservative management:
An antibiotic – broad-spectrum antibiotic is given to prevent cholangitis.
Analgesic –
Antispasmodic drugs –
Anticholinergic – given to relax the sphincter of Oddi.
Glucose iv or orally given
Surgical management:
Stone extraction by surgery
Lithotripsy
Cholecystectomy
Biliary endoscopic Sphincterotomy
Biliary stenting.
What are the preventions of choledocholithiasis?
Physical activity – avoid a sedentary lifestyle. Make routine exercises regularly.
Take a High fiber diet
Take Low cholesterol diet
Avoid prolonged fasting.
Health Disclaimer







No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any comment regarding my blog please let me know